THE TUNDRA!
2.16.2012
Anthropogenic Threats
Impact from Human Workings on the Tundra Environment
Housing development doesn't seem to be a major problem in the
Tundra, with the weather being cold and all. It is seemingly a technical
challenge to use efficient sewage treatment in a cold environment. The biggest
threats of humans to the tundra are airborne pollutants, which have brought DDT
and PCB's (industrial wastes) to even the most remote areas in this region.
The biggest threat of all comes from oil and gas development.
The Arctic National Wildlife just so happens to be sitting on top of an about 6
month supply of oil.
Despite the great difficulty of extracting this oil,
corporate interests still persist to drill here. Global warming also plays a
key role in the future of the tundra biome as the planet warms up, the
permfrost will continue to melt and tundra ecosystems will fall apart. Inside
the permafrost as well, is dead plant material which will release CO2 into the
atmosphere upon decaying, thus accelerating global warming.
Soil and Ground Conditions
When snow above the
active layer melts, the water remains on the surface of the soil. Water cannot
be absorbed by the permafrost (layer of permanent frozen ground below the
active layer) and leaves the top layer wet and soggy. Evaporation of water is
also impossible because of the tundra's cool air. The arctic tundra landscape
is formed from the freezing and refreezing of this soggy soil. There are five
distinguishable types of land formations by freezing water: pingos, frost
boils, bumpy ground, polygons, and stripes.
Pingos are hills formed by pools of
water that were trapped by permafrost and polygons are geometric land shapes
outlined by cracks filled with water. The process, in which the water causing
the tundra's soggy ground flows downhill, is called solifluction.
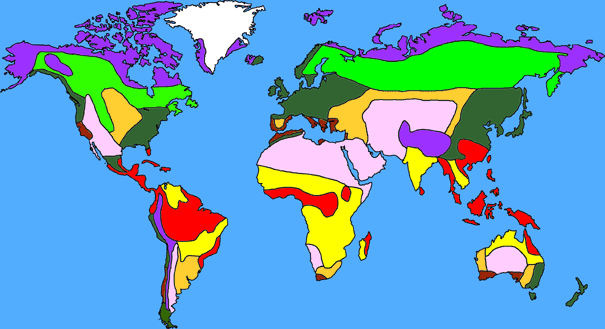
Where is the Arctic Tundra?
Tundra Climate
It is mainly located in the poleward region of about 60 degrees North latitude. The average temperature of the tundra per year is 16 degrees F. The highest, warmest temperature it can get is 45 degrees and the coldest is 10 degrees below 0. This biome is made up of most of the earth's coldest regions on Earth.
It is mainly located in the poleward region of about 60 degrees North latitude. The average temperature of the tundra per year is 16 degrees F. The highest, warmest temperature it can get is 45 degrees and the coldest is 10 degrees below 0. This biome is made up of most of the earth's coldest regions on Earth.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)